一、如何使用swipe
https://github.com/bradbirdsall/Swipe
二、swipe源码
- 有3个div,如下

- 以图中1的位置为index,修改div的left,让所有的div都叠放在index位置上,如图

- 用transform来移动index-1,和index+1的,分别位于index的左右两边

- 不断的循环第二步
- 当n>3时,因为,每次需要处理的只有3块div,仍然可以如上处理
- 当n==2时,将这两块div复制一遍
- 当n==1时,固定不动
https://github.com/bradbirdsall/Swipe



- isolate_namespace
- app
- routes
- initializers
用命名空间来隔离不同的engine
An instance of ActionDispatch::MiddlewareStack used to store middlewares.
An instance of ActionDispatch::Routing::RouteSet used to store routes.
有如下这些initializers:
set_load_path before: :bootstrap_hook
#将configred load paths 添加到 ruby load paths
initializer :set_load_path, before: :bootstrap_hook do
_all_load_paths.reverse_each do |path|
$LOAD_PATH.unshift(path) if File.directory?(path)
end
$LOAD_PATH.uniq!
end
set_autoload_paths :bootstrap_hook
#暂时不能理解,简单的认为是那些自动加载的文件
#包括["app","app/controllers", "app/helpers", "app/models",
# "app/mailers", "app/controllers/concerns", "app/models/concerns"]
initializer :set_autoload_paths, before: :bootstrap_hook do
ActiveSupport::Dependencies.autoload_paths.unshift(*_all_autoload_paths)
ActiveSupport::Dependencies.autoload_once_paths.unshift(*_all_autoload_once_paths)
# Freeze so future modifications will fail rather than do nothing mysteriously
config.autoload_paths.freeze
config.eager_load_paths.freeze
config.autoload_once_paths.freeze
end
add_routing_paths
#加载路由文件
initializer :add_routing_paths do |app|
paths = self.paths["config/routes.rb"].existent
if routes? || paths.any?
app.routes_reloader.paths.unshift(*paths)
app.routes_reloader.route_sets << routes
end
end
add_locales
#I18n文件
initializer :add_locales do
config.i18n.railties_load_path.concat(paths["config/locales"].existent)
end
add_view_paths
#views文件为lazily load files
#用ActiveSupport.on_load(name, options, block),定义一个名为name的lazily load hook
#之后可以ActiveSupport.run_load_hooks(name, base)来加载(让base来调用block)
initializer :add_view_paths do
views = paths["app/views"].existent
unless views.empty?
ActiveSupport.on_load(:action_controller){ prepend_view_path(views) if respond_to?(:prepend_view_path) }
ActiveSupport.on_load(:action_mailer){ prepend_view_path(views) }
end
end
load_environment_config before: :load_environment_hook, group: :all
#加载environments文件
initializer :load_environment_config, before: :load_environment_hook, group: :all do
paths["config/environments"].existent.each do |environment|
require environment
end
end
append_assets_path, group: :all
#加载assets文件
initializer :append_assets_path, group: :all do |app|
app.config.assets.paths.unshift(*paths["vendor/assets"].existent_directories)
app.config.assets.paths.unshift(*paths["lib/assets"].existent_directories)
app.config.assets.paths.unshift(*paths["app/assets"].existent_directories)
end
prepend_helpers_path
#加载helpers文件
initializer :prepend_helpers_path do |app|
if !isolated? || (app == self)
app.config.helpers_paths.unshift(*paths["app/helpers"].existent)
end
end
load_config_initializers
#加载config/initializers文件
initializer :load_config_initializers do
config.paths["config/initializers"].existent.sort.each do |initializer|
load(initializer)
end
end
engines_blank_point
#空白的initializer
SampleApp::Application < Rails::Application < Rails::Engine < Rails::Railtie
这里需要注意的地方有下面二个
源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
将 instance methods 委托给 class 使用
我的理解是:有序的对类进行初始化。参考TSort。
来看个例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | |
最后的输出结果如下:
"0: Went to USA-Silicon Valley and "
"1: Went to Britain-London and "
"2: Went to China-Beijin and "
"3: Went to France-Paris and "
拓扑排序
对一个有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph简称DAG)G进行拓扑排序,是将G中所有顶点排成一个线性序列,使得图中任意一对顶点u和v(一条有向边可以表示为(u, v)),若 ∈E(G),则u在线性序列中出现在v之前。
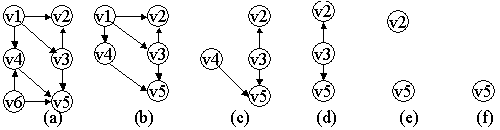
如上图所示,图(a),排序后的结果是:6, 1, 4, 3, 2, 5
排序的结果不是唯一的,图(a)排序后的结果还可以为1, 6, 3, 2, 4, 5
常用的算法是“入度为零”的算法,上图的图(a)到图(f)的过程就是使用入度为零的一个过程
- 从有向图中选取一个没有前驱的顶点,并输出之 (入度为零,如图a的v1,v6);
- 从有向图中删去此顶点以及所有以它为尾的弧;(如图a,输出v1或v6后,要相应的删除以它为顶点的边{(v1, v2), (v1, v3), (v1, v4)}或{(v6, v4), (v6, v5)})
- 重复上述两步,直至图空,或者图不空但找不到无前驱的顶点为止。
借用api的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
tsort_each_node和tsort_each_child是必须rewrite的两个方法
TSort根据tsort_each_node得到每个节点,根据tsort_each_child得到节点的子节点
如上图a的,通过tsort_each_node分别得到 v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6;通过tsort_each_child v1得到 v2, v3, v4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | |
上面的例子中,如果 “v1.5”没有{before: “v2”},得到的结果”v1.5”会在最后面,这是因为{after: “v1”},可以在v1后面的任意位置